It’s frustrating when your computer’s internet is fast, but your phone’s connection crawls at a snail’s pace. While some difference in speed between devices is normal, it shouldn’t be huge. If you notice a decent difference in speed between your phone and computer, here are some possible reasons.
1 You’re Connected to a Different Network
Before diving into why your phone’s internet is slower, ensure you’re connected to the same network as your computer. I often find my smartphone automatically connecting to a different, slower hotspot connection instead of my main Wi-Fi when I notice a big drop in speed.
If your devices are on different networks, you’re bound to see a difference in internet speed. Most devices allow you to set a preferred Wi-Fi network, so they connect directly to it even when other networks are available. To ensure your phone gets the same speed as your laptop, ensure the same network is configured as the preferred option.
2 You’re Using Your Phone and Computer at Different Times
The more devices connected to your network, the less bandwidth each gets, leading to slower internet speeds. So, if your computer has decent speed during the day, but your phone slows down in the evenings or weekends, it could be due to network congestion from multiple devices, like kids or other family members using the internet simultaneously.
To prevent your phone from competing for bandwidth, you can ask your family members to disconnect any unused devices from the internet. If everyone is using a single device, your current internet plan may not be sufficient. In that case, upgrade your internet plan for more bandwidth or get a better router to support more devices on the same network.
3 It’s Ethernet Versus Wi-Fi
If your computer is connected to the router via an Ethernet cable while your phone is on Wi-Fi, the difference in connection type might explain the slower speed on your phone.
Wi-Fi can be affected by many things, like electromagnetic devices, walls, distance from the router, or interference from other connected devices. These factors weaken the signal and can lead to slower internet speeds. In contrast, an Ethernet connection is directly linked to the router, avoiding the issues Wi-Fi faces. I’ll show you how to deal with individual Wi-Fi issues shortly.
4 You’re Too Far From Your Router
The closer your device is to the router, the better your internet speed will be. The connection weakens as you move farther away or if there are physical barriers like walls or floors. So, if your router is near your computer, but you use your phone farther away, you’re likely to experience slower speeds.
If your internet slows down significantly when you’re upstairs or in the backyard but works fine when you’re in the same room as the router, the distance might be the problem. To fix this, place your router in a spot that offers a stable connection to all the areas where you use your phone without affecting the signal for your computer.
5 The Wi-Fi Frequency Band Could Be the Culprit
Wi-Fi networks usually operate on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band covers a larger area but is slower, while the 5 GHz band offers faster speeds but has a shorter range. Both devices must operate on the same frequency band to achieve the same speed.
If your phone doesn’t support the 5 GHz band, it will default to the slower 2.4 GHz connection. To verify this, check the device’s specifications using its model number. If it doesn’t mention dual-band or 5 GHz, it’s not compatible. On the other hand, if your computer is connected to the 5 GHz band, you’ll likely notice a significant difference in speed.
Even if your phone supports 5 GHz, being far from the router can weaken the signal, causing the router to automatically switch your phone to the 2.4 GHz band for a more stable connection. Staying closer to the router can improve your speed if your phone supports 5 GHz. If it doesn’t, you may need to upgrade your phone to a device that does.
Some routers run the two Wi-Fi bands as separate networks, so you might have added one but not the other on your phone, which means the phone won’t switch to the other band. So ensure you’ve logged in to both.
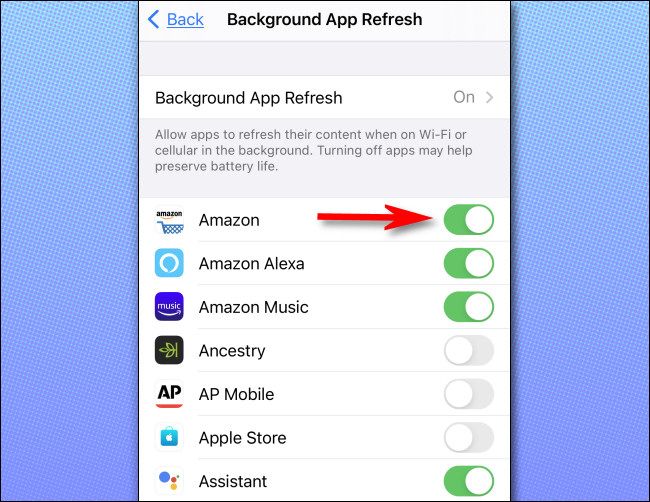
6 Background Apps on Your Phone Are Hogging Your Data
You may have apps on your phone that continue to run in the background and use bandwidth even when you’re not actively using them. Your email client might be syncing messages, social media apps updating feeds, or other apps tracking notifications. Plus, we often leave some unused apps open, adding extra strain on our network connection.
While computers also run background processes, phone hardware typically falls short in network stability compared to computers with faster network cards. We also manage network resources better on our computers but often overlook this on our phones. Also, you might have more apps running on your phone, leading to slower speeds for other tasks.
To improve your experience, check your phone’s settings and limit background data usage to free up bandwidth.
7 Your Phone Is Set as a Low-Priority Device
Some advanced routers have a Quality of Service (QoS) feature that allows you or network administrator to prioritize devices for internet bandwidth. If a device is set to a lower priority, it will receive less bandwidth than higher-priority devices, hence slower internet speeds, especially during peak usage times.
If you manage your router settings yourself, you can adjust the QoS priority to make your phone equal to or higher than your computer for improved speed. If someone else manages your router, they may have set your phone to a lower priority while treating your computer as a high-priority device. Often, you might not even be aware of such limitations.
You can kindly discuss your concerns with the network administrator, and they may remove the limitation for your device, allowing you to enjoy faster internet again.
8 A VPN or Proxy Server Is Slowing Down Your Connection
If you don’t use a VPN on your computer but do on your smartphone, that can slow down your connection. When you connect to the internet through a VPN, your data routes through an additional server, which adds latency and reduces speed. The speed drop can be more noticeable if you use a low-quality VPN service or a server far from your location.
If you use the same VPN service on both devices but notice better speeds on your computer, it may be because the computer’s more powerful hardware handles encryption and decryption more efficiently, minimizing the impact on internet speed. To check if the VPN is the issue, try disconnecting from it and see if your speed improves. If disconnecting the VPN improves speed, upgrade to a better VPN service or stop using it.
These are a few reasons why your phone’s internet may be slower than your computer’s. By examining each possibility individually, you should be able to identify the main cause of the slowdown and fix the issue. If the problem is due to network congestion or an outdated router, you may need to upgrade your router or internet plan.
Source link